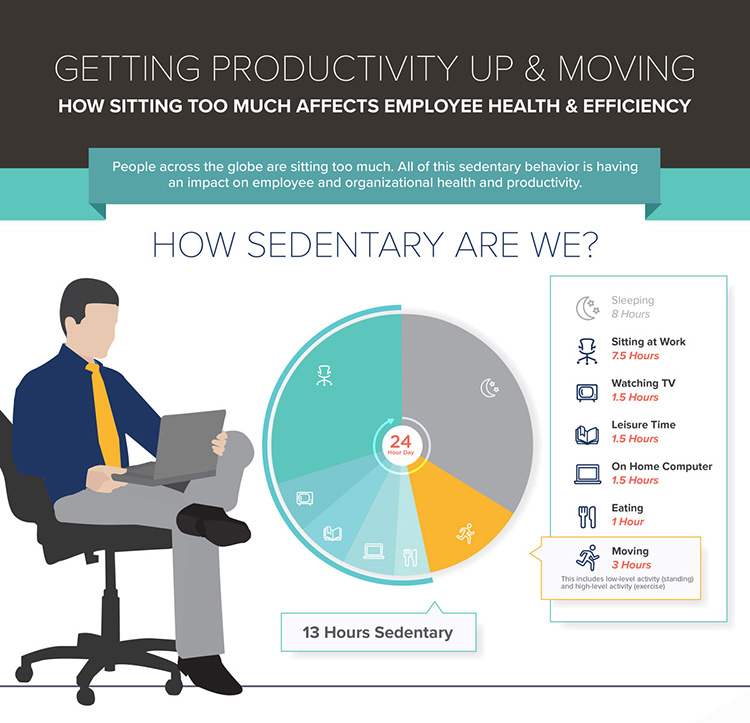
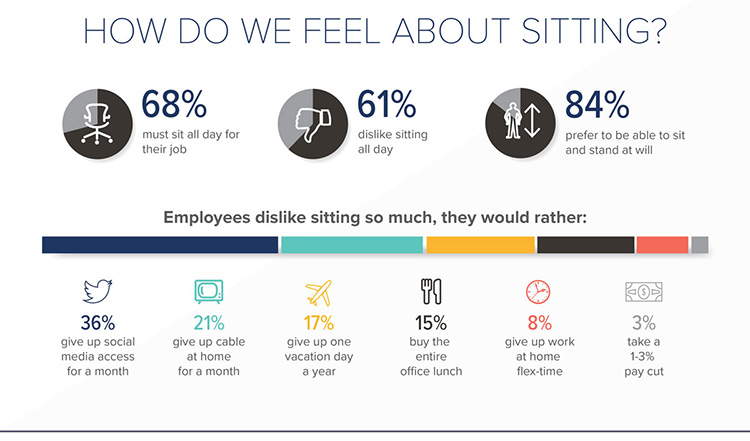
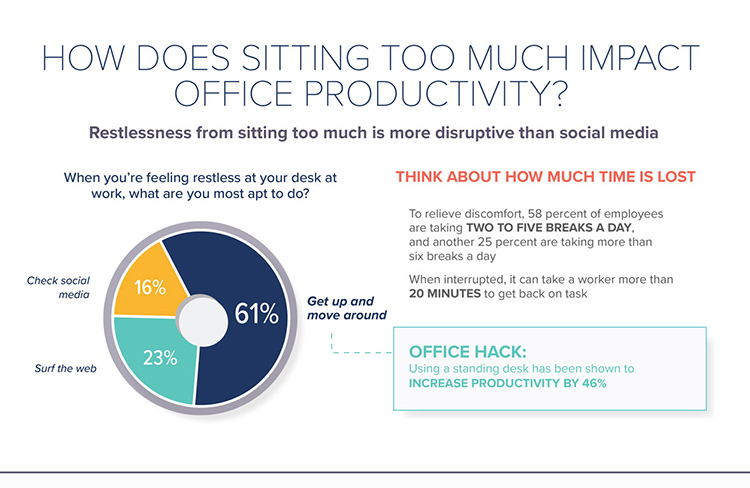
1. Physical health issues: Prolonged sitting has been linked to various physical health problems, including obesity, cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, musculoskeletal disorders, and certain types of cancer. Lack of physical activity can lead to weight gain and increased risk of chronic conditions, which can negatively impact employee health and overall well-being.
2. Musculoskeletal problems: Sitting for long periods can contribute to musculoskeletal issues such as back pain, neck strain, and poor posture. Remaining in a sedentary position for extended durations can place undue stress on the spine, shoulders, and neck, leading to discomfort and decreased productivity.
3. Reduced metabolic rate: Sitting for hours at a time leads to a decrease in metabolic rate, resulting in lower calorie burning and reduced circulation. This can contribute to weight gain and a sluggish feeling, affecting employee energy levels and focus.
4. Mental health concerns: Prolonged sitting can also have a negative impact on mental health. Sedentary behavior has been associated with an increased risk of depression, anxiety, and other psychological issues. Moreover, remaining seated for extended periods without breaks or movement can lead to feelings of lethargy, decreased motivation, and decreased cognitive function.
5. Reduced productivity and engagement: Sitting for prolonged periods without movement can lead to decreased productivity and engagement levels. Employees may experience difficulty in maintaining focus, concentration, and creativity, resulting in reduced efficiency and overall performance.
To mitigate these negative effects, it's important for employees to incorporate regular physical activity and movement breaks into their work routine. Encouraging standing or walking meetings, providing adjustable workstations that allow for both sitting and standing, promoting active breaks, and creating a workplace culture that values movement and employee well-being can all contribute to a healthier and more efficient workforce.